How to calculate MD5/SHA1/SHA256 checksums of a file without an external tool
Please let our ADS show!
This sites offers only FREE software and it's supported by a few advertisement boxes (no intrusive popups).
Please:
- disable your AdBlocker by adding CoolSoft website to whitelist
- give the proper cookie consent
- enable JavaScript for this website
This seconds wait is to let you update your browser configuration...
Ok, I've done the required changes... now show me your content!Checksum is the easiest way to check if the content of a file is as it was expected to be or was changed/broken after a file transfer or an internet download.
A lot of websites (like CoolSoft) show the expected MD5/SHA1/SHA256 checksums beside each download link, so users can check "download health" after it completes.
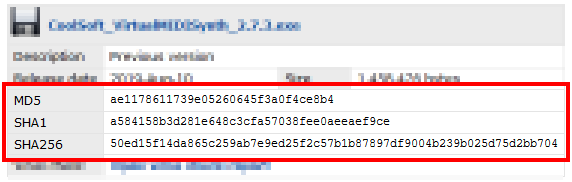
After downloading a file you must calculate its checksum and compare it with the one reported beside the file; if they are the same (you could also check only the first/last 8 chars) then you can be sure that the downloaded file is not corrupted.
There's a lot of free utilities available to calculate the checksum of a file, but you could also do it with a tool already bundled in your Windows installation: certutil.
- open Windows Explorer (Win+E) and go to the folder containing the downloaded file
- while pressing the SHIFT key right click on an empty space into the folder
- now choose "Open Powershell window here..." or "Open command prompt here"
- a command prompt will open into the selected folder
- now finally run certutil and make it calculate the required checksum (replace filename.exe with the filename you're going to check):
PS C:\testFolder> certutil -hashfile filename.exe MD5 MD5 hash of filename.exe: 2ffefb74864d962ef9fabde17031a4e7
PS C:\testFolder> certutil -hashfile filename.exe SHA1 SHA1 hash of filename.exe: ade2405a022628835feac342c642a9113f630271
PS C:\testFolder> certutil -hashfile filename.exe SHA256 SHA256 hash of filename.exe: 4cc28a5be8dc7425a4c4fd23a75ca392f18be35d70232e777dce6d9f3b4d79ac
Supported checksums are: MD2, MD4, MD5, SHA1, SHA256, SHA384 and SHA512.
Navigazione
Login
Clicca qui per supportare il mio lavoro con PayPal
oppure offrimi un caffè
